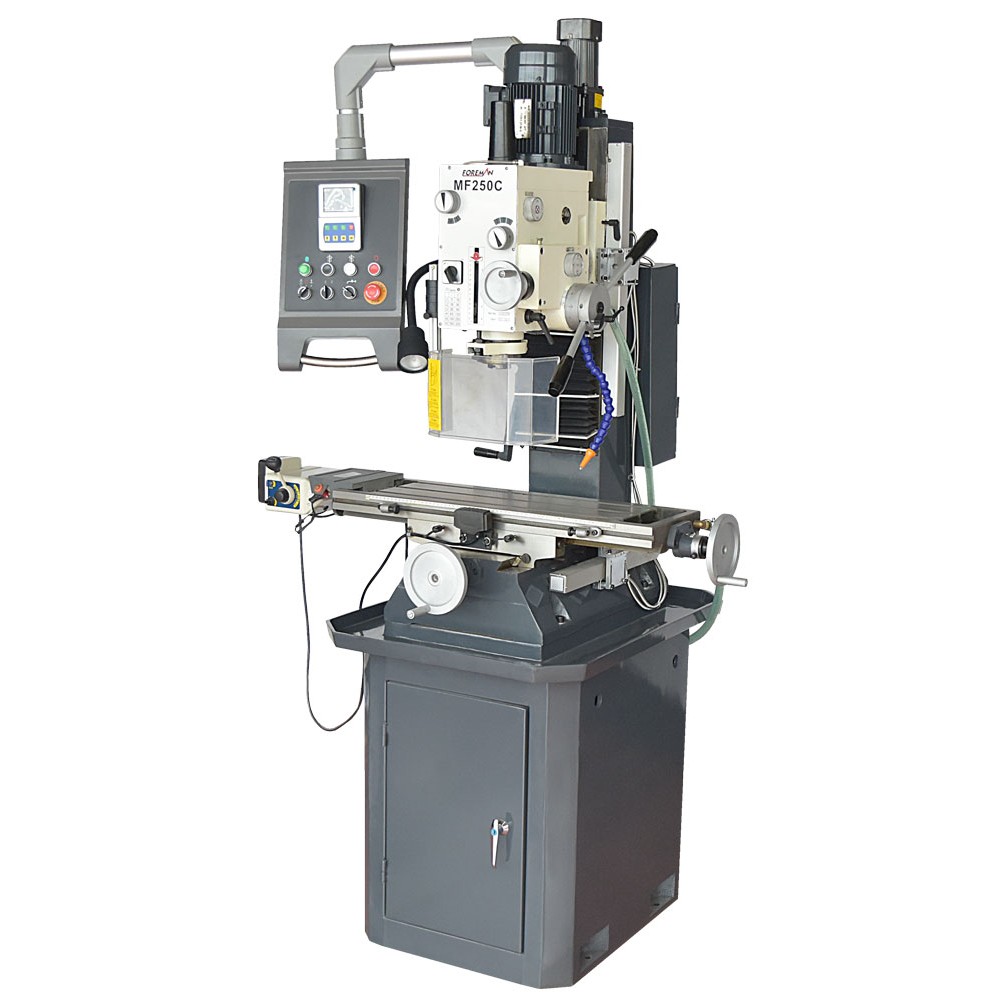
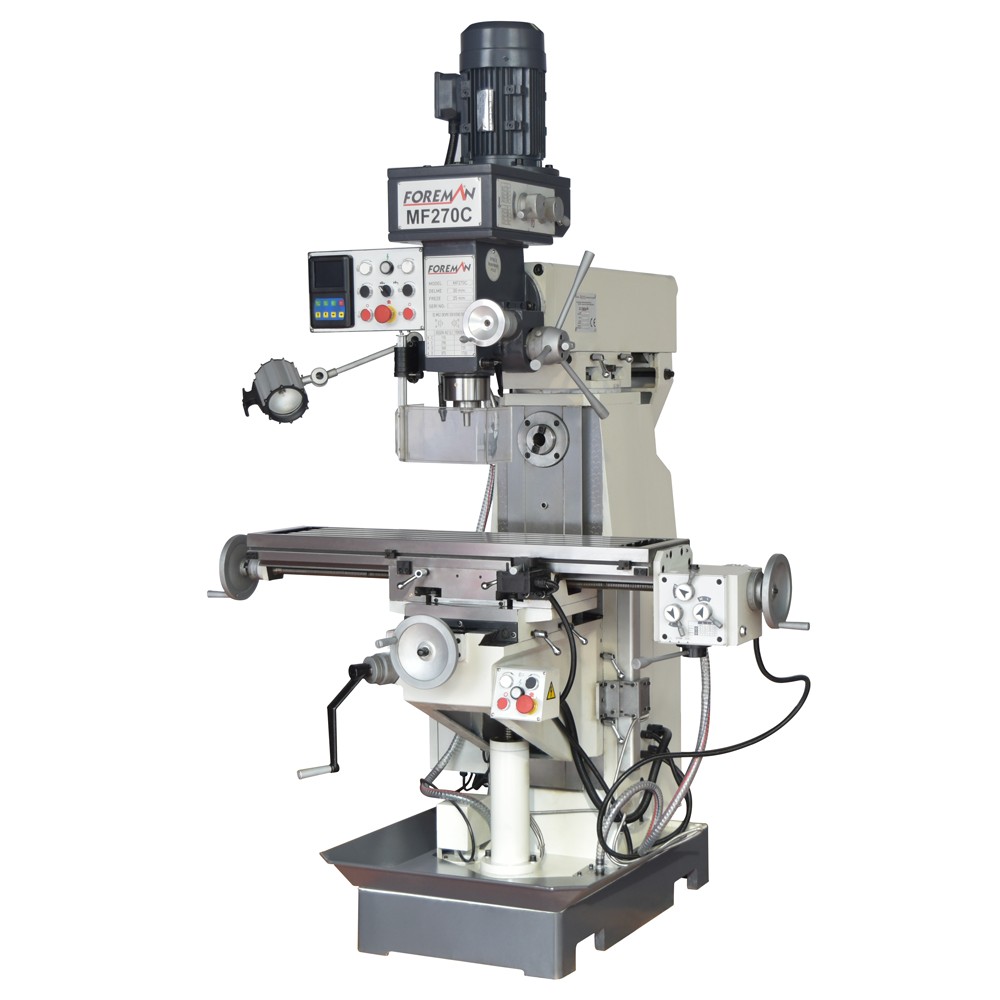
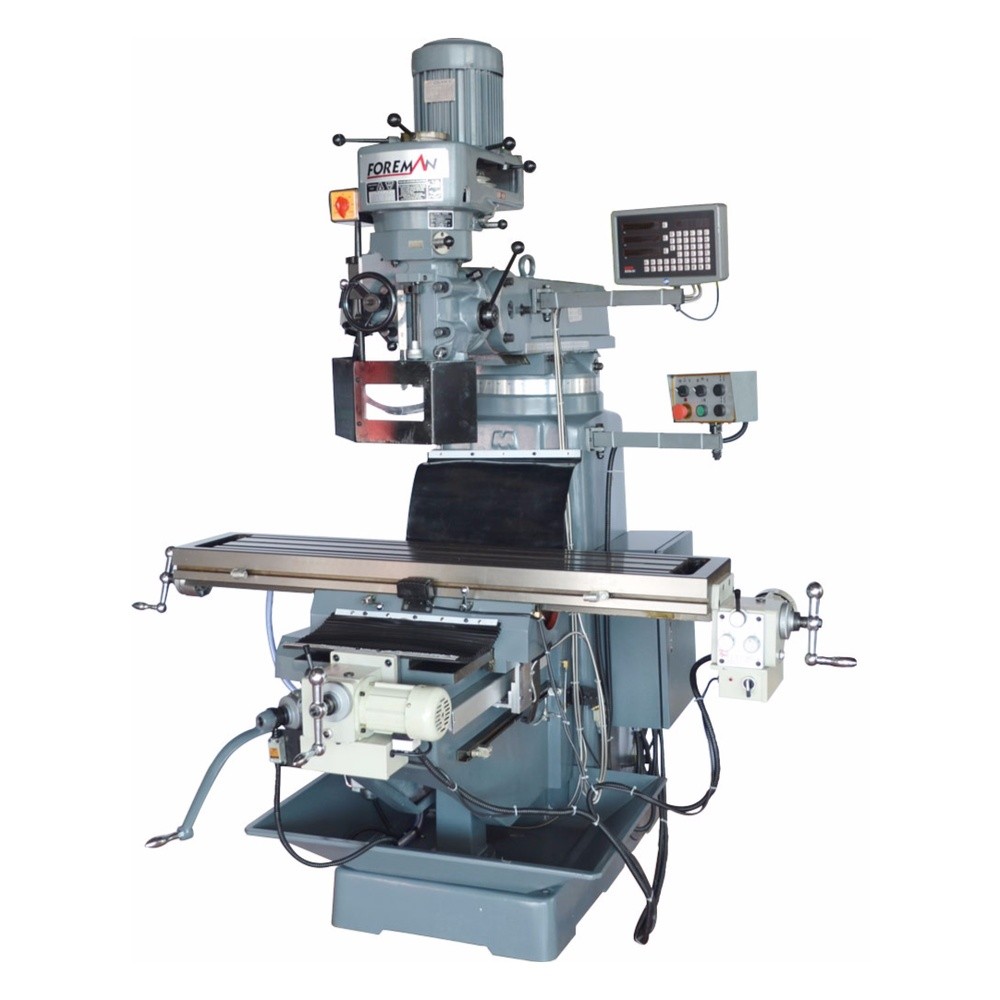
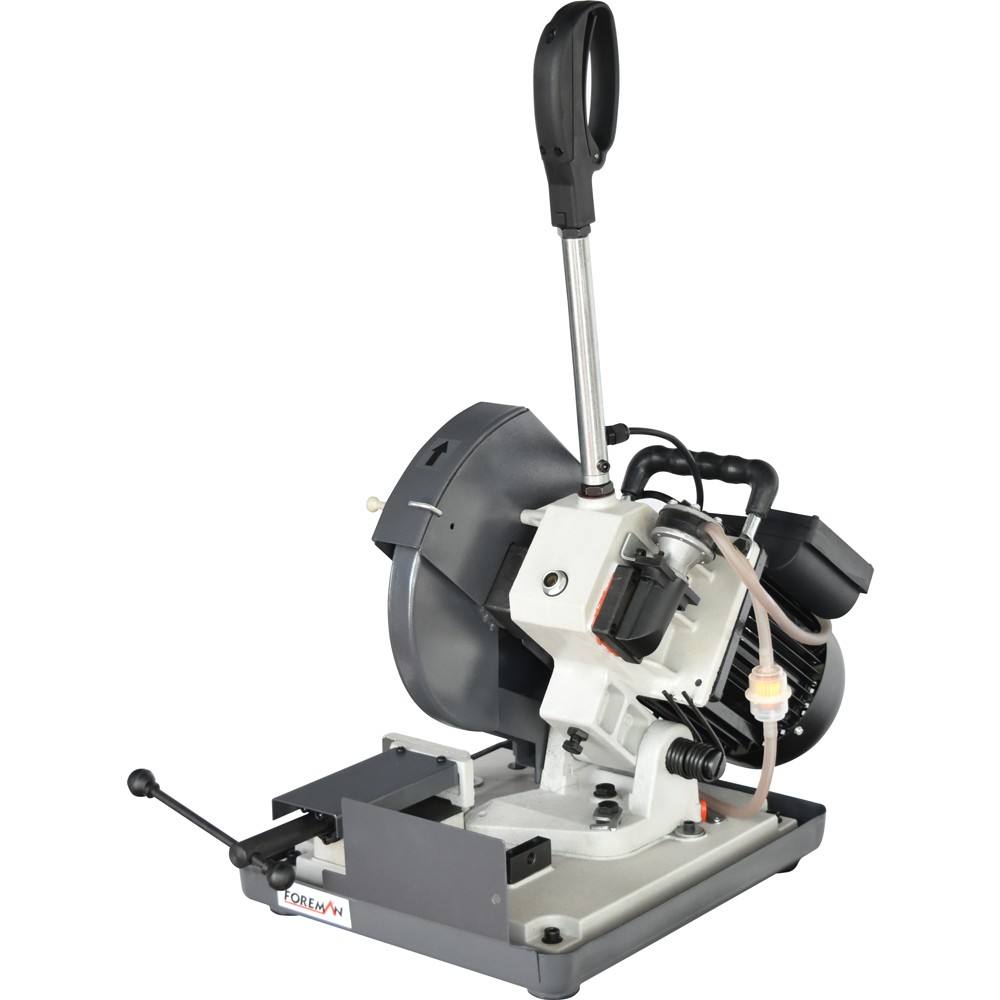
Two Angle Swivel (5 Axis) Ram Head
X, Y, Z Axis Travels 1300x320x480 mm
3 Axis Automatic Feeding (Servo Transmission)
Vertical and Horizontal Spindle ISO50
5.5 Kw (Vertical) 4 kW (Horizontal) Motor Power
Spindle Movement with Inventor
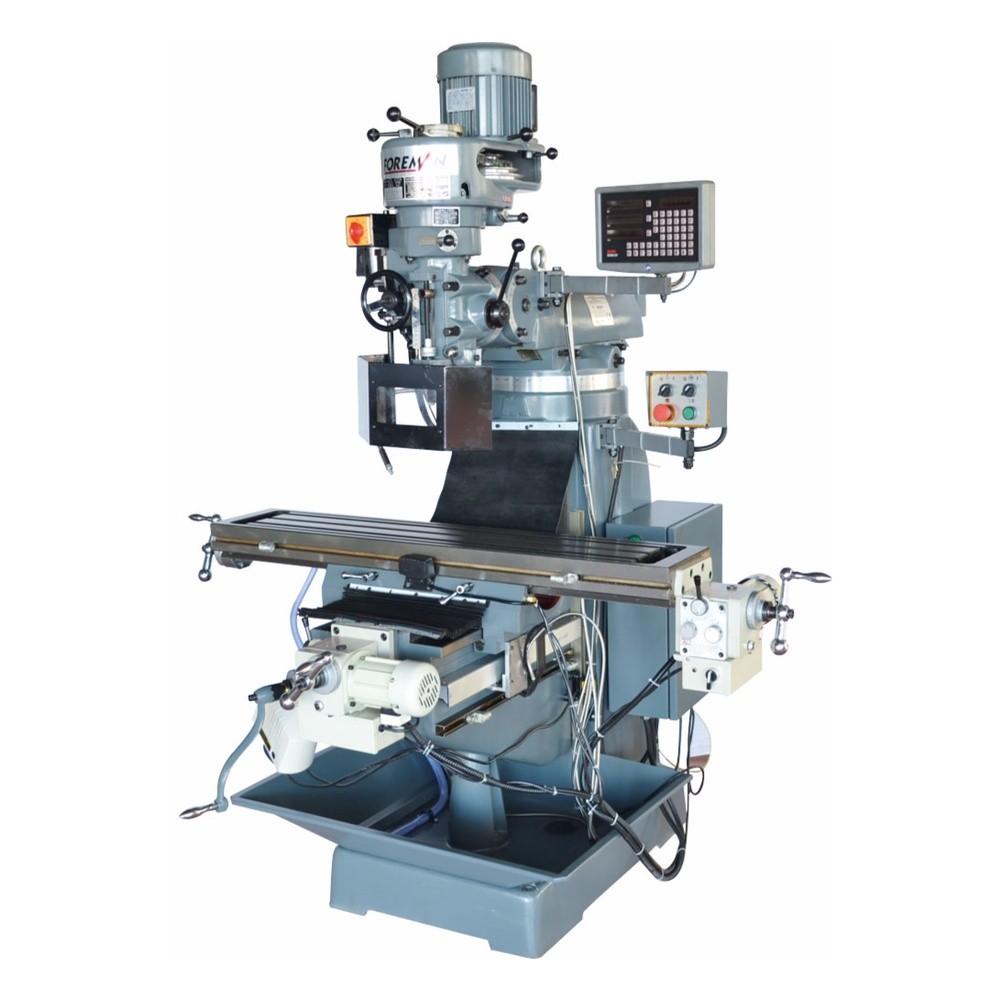
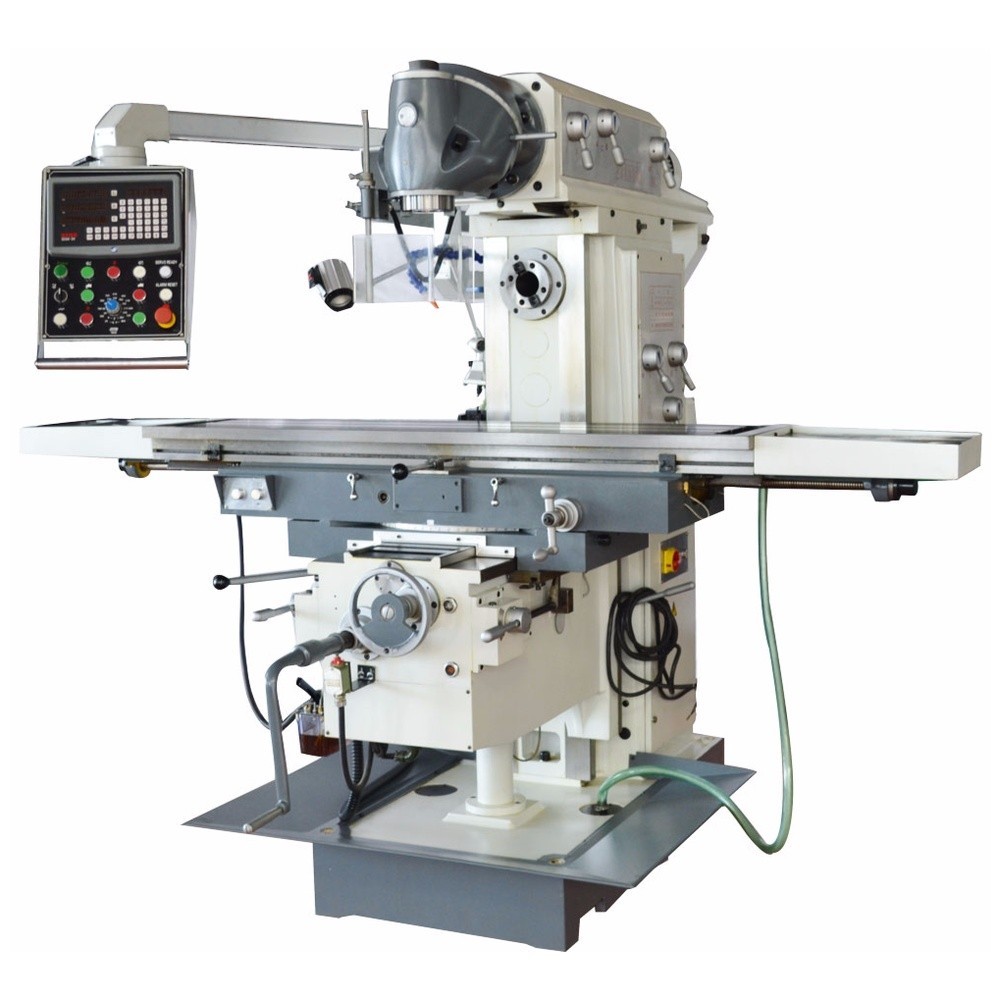
X-Y-Z Axis Movements 1200x400x500 mm
3 Axis Automatic Feeding (Servo Transmission)
Vertical Spindle ISO50
7.5 kW Engine Power
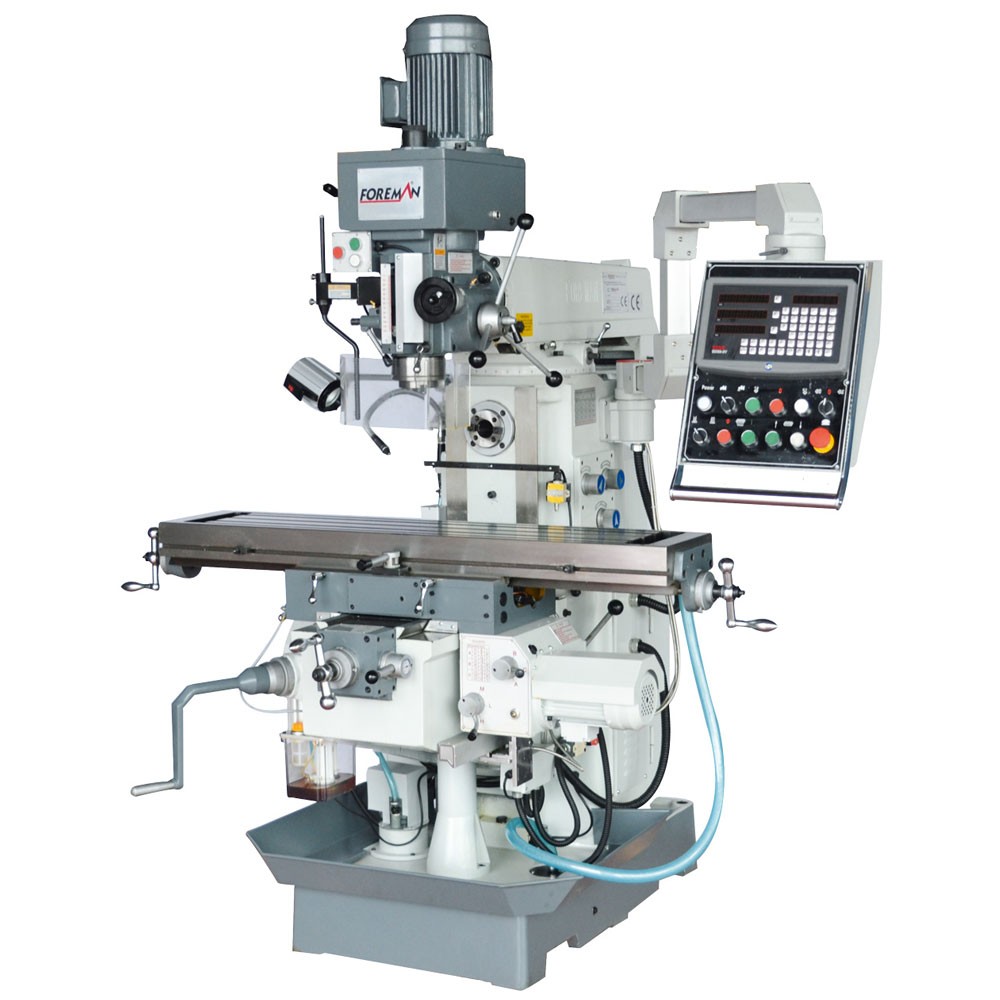
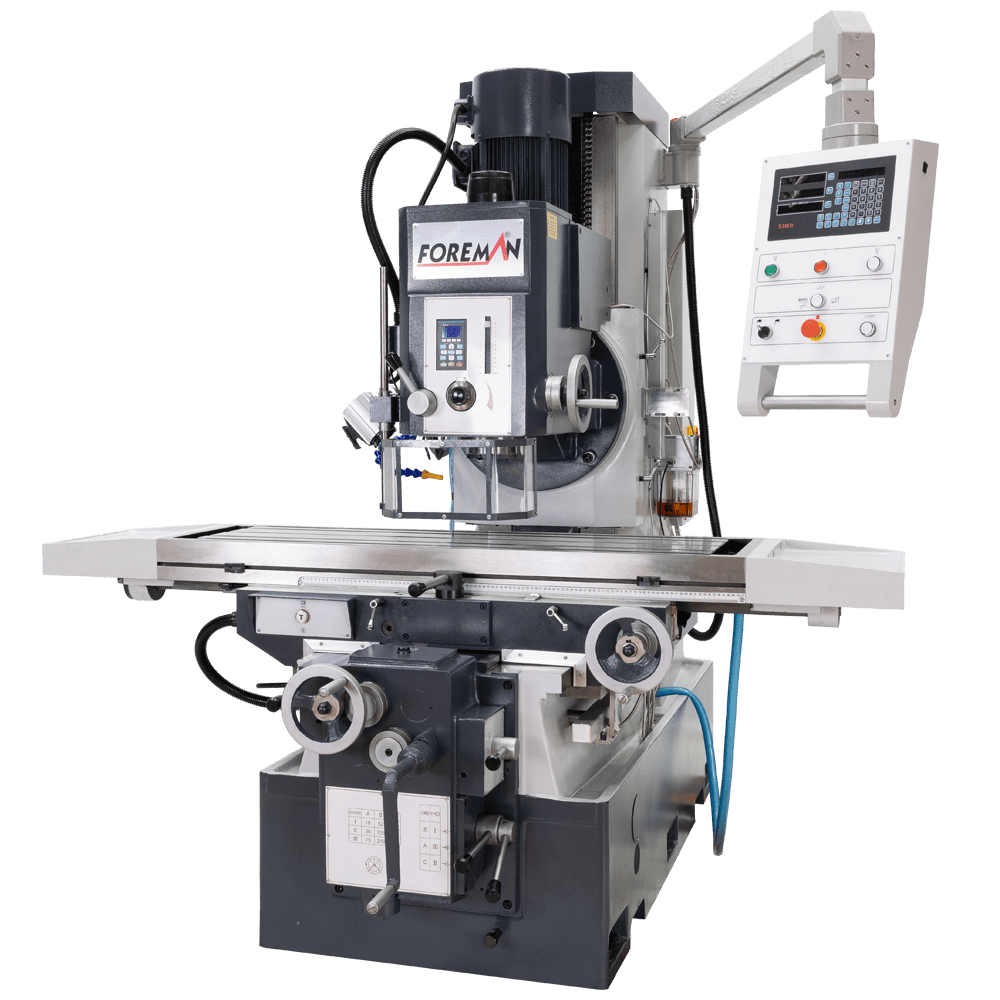
High Torque Gearbox Head
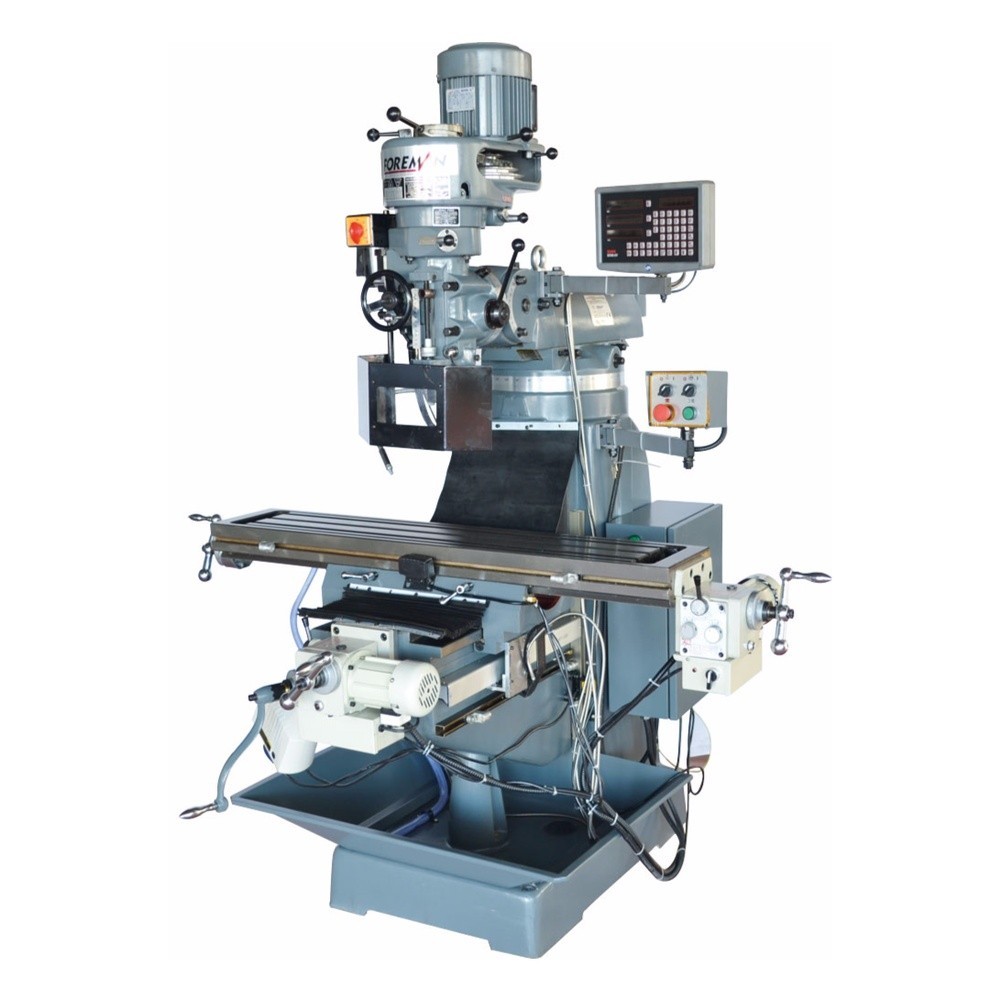
X, Y, Z Axis Movements 1500x620x550 mm
3 Axis Automatic Feeding (Servo Transmission)
Vertical Spindle ISO50
6.5 kW Engine Power
SIK SORULAN SORULAR
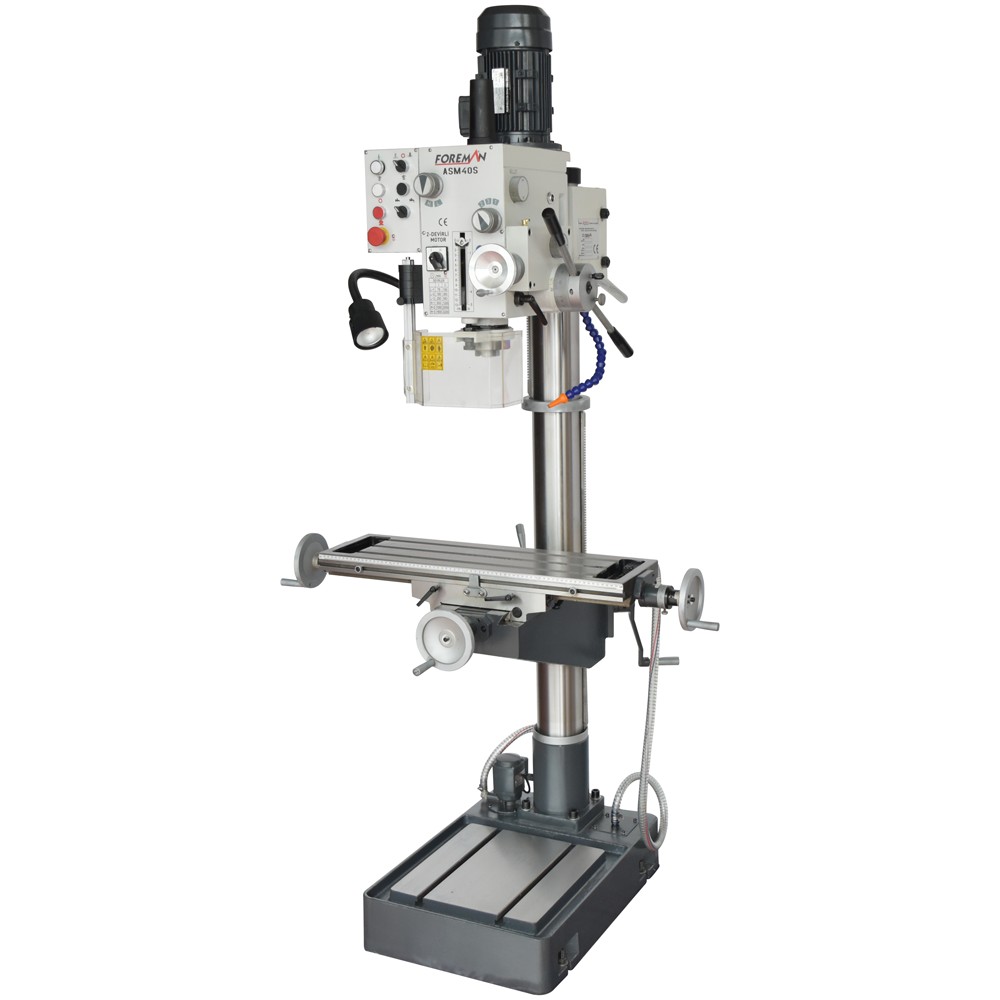
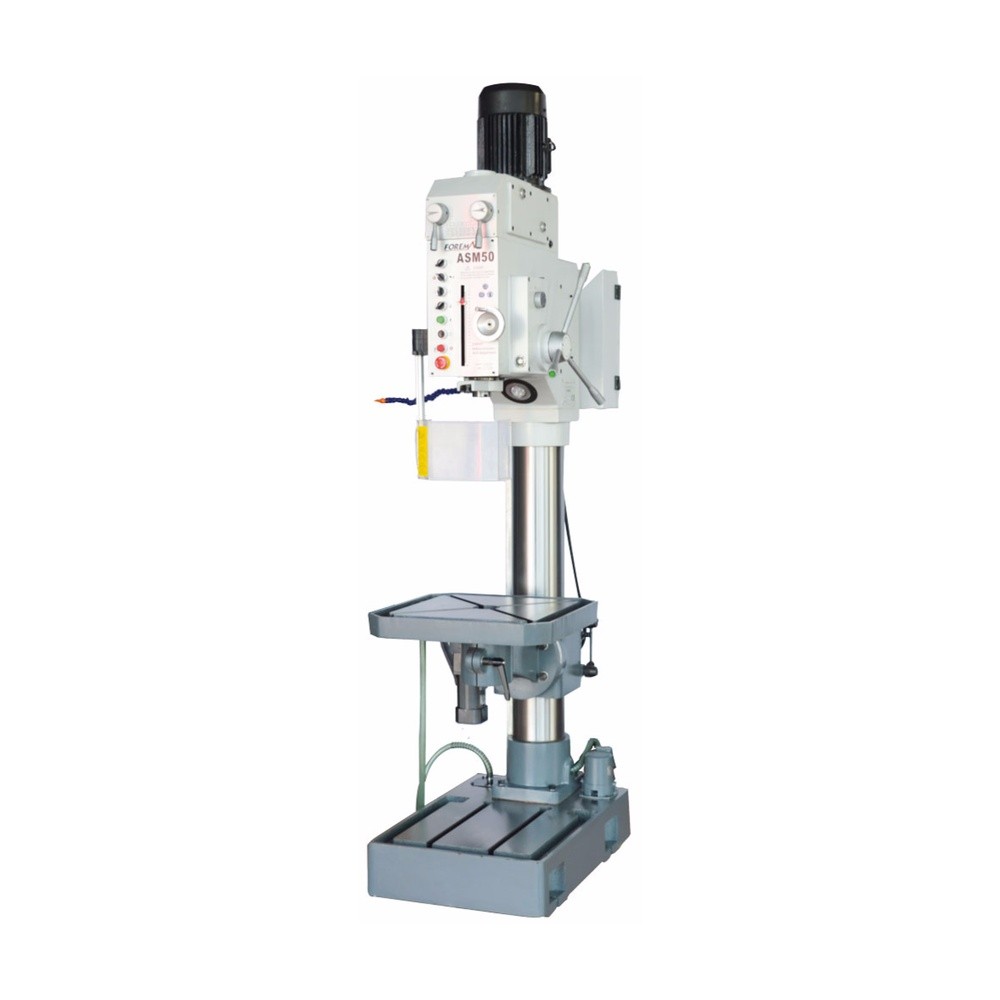
The working principle of the vertical milling machine is as follows:
Machine Setup:
Firstly, the workpiece is fixed to the table. This is done using a vice or clamps.
The cutting tool is placed in the tool holder and clamped firmly in the correct position.
Setting the Cutting Tool:
The cutting tool is mounted on the milling spindle. The milling spindle is in vertical position and the cutting tool rotates around the spindle. The height and position of the cutting tool relative to the workpiece are adjusted.
Setting Process Parameters:
Cutting speed (rotation speed of the cutting tool) and feed rate (the speed at which the workpiece passes under the cutting tool) are determined. These parameters are set according to the material type and cutting tool type.
Starting the Machine:
The vertical milling machine is started and the milling spindle starts to rotate. The workpiece is brought under the cutting tool on the moving table. In some machines, the table moves automatically, while in others the operator moves the table manually.
Milling Process:
The cutting tool creates the desired shape by removing material from the surface of the workpiece.
The cutting tool cuts at a certain depth as it passes over the workpiece. The depth and shape of the process depends on the movement and position of the cutting tool.
Cooling and Lubrication:
During the process, coolants are used to reduce the heat generated between the cutting tool and the workpiece and to extend the life of the cutting tool. These fluids are sprayed on the cutting tool to reduce the temperature and make the cutting tool work more efficiently.
Finishing:
When the process is completed, the machine is stopped and the workpiece is removed from the table.
If necessary, additional operations are performed until the workpiece reaches the desired dimensions and surface quality.
These steps summarise the general working principle of the vertical milling machine. Depending on the machine and workpiece, there may be some variations in these steps.
Vertical milling machines can be used extensively in the processing of steel, aluminium, brass, stainless steel and cast iron material types. They are also preferred for machining plastic, composite and wood materials. Thanks to their versatility and precision, vertical milling machines can be used for processing different materials in many industrial and commercial applications.
Vertical milling machines have several advantages:
High Precision: Vertical milling machines can cut with high precision and accuracy, which is a great advantage in complex and detailed operations.
Versatility: Different operations can be performed using various cutting tools. Suitable for machining different materials and creating various shapes.
Machining Complex Shapes: Complex geometric shapes and profiles can be machined thanks to the cutting tool working in the vertical position.
Easy Adjustment and Operation: Vertical milling machines are relatively easy to use and adjust. The positions of the cutting tool and workpiece can be adjusted quickly and precisely.
High Productivity: High speed and continuous production can be achieved with manual or automatic feed options.
Flexible Processing Capacity: It is possible to process different materials such as metal, plastic, wood. This flexibility makes the machine suitable for many industrial applications.
Better Viewing Angle: The operator can better see the interaction between the cutting tool and the workpiece, which provides better control during the process.
High Power and Durability: Vertical milling machines are generally strong and durable, which ensures high performance even on heavy duty jobs and large parts.
Various Application Areas: It has a wide range of applications in many sectors such as automotive, aerospace, mould making, furniture production.
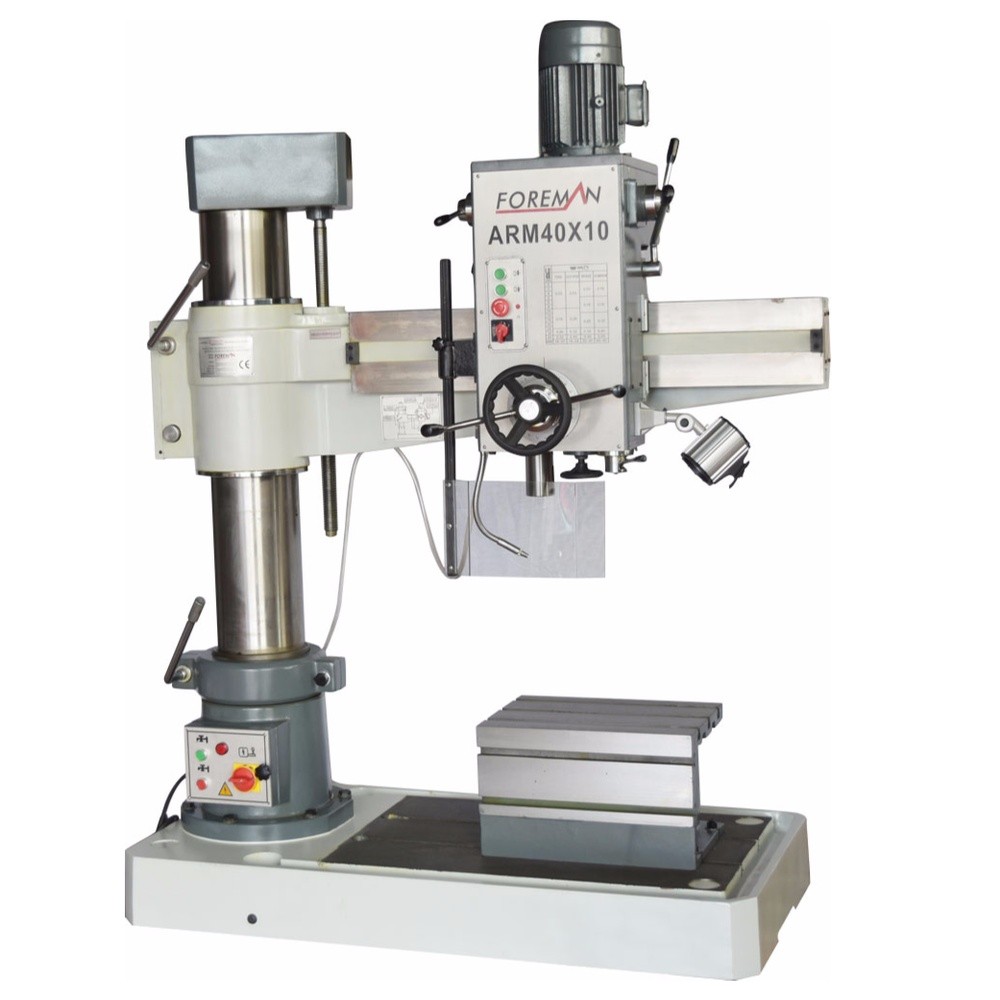
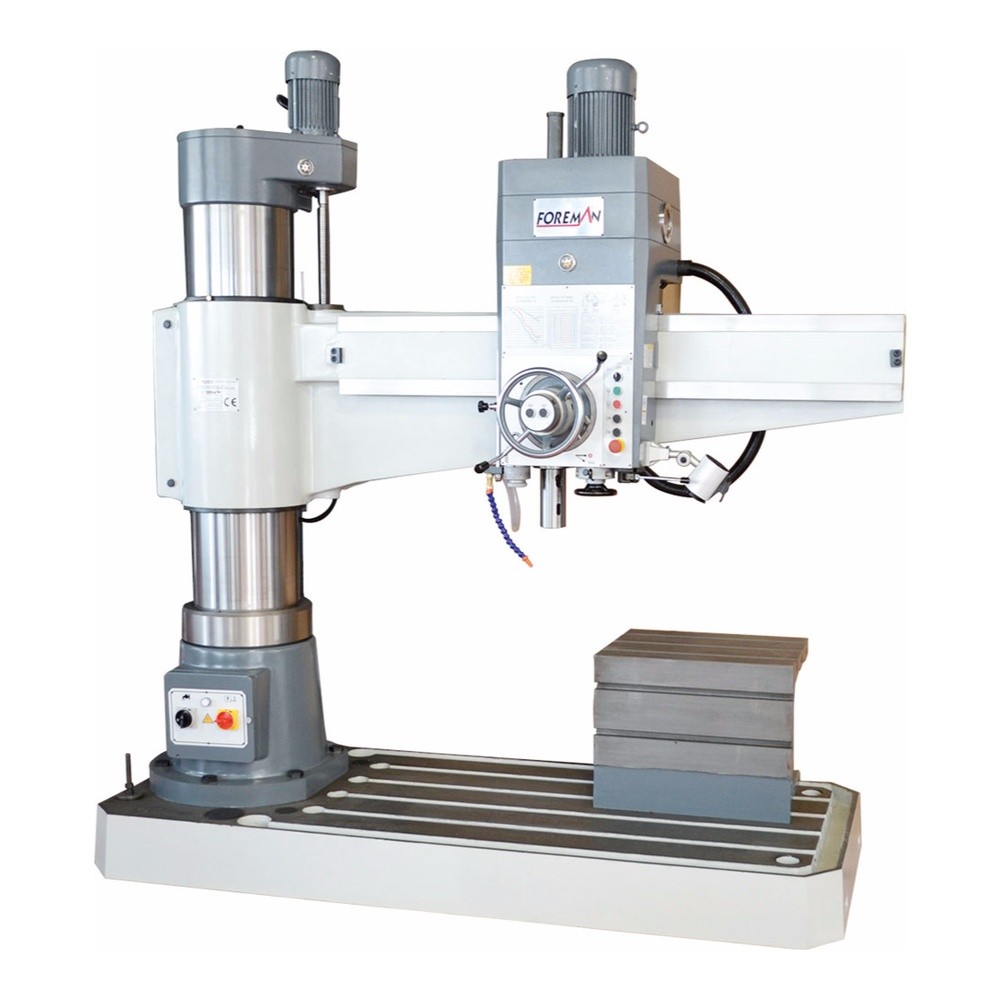
The main differences between vertical milling machines and horizontal milling machines are as follows.
Cutting Tool Position:
Vertical Milling Machine: The cutting tool is in vertical position and moves on the vertical axis.
Horizontal Milling Machine: The cutting tool is in horizontal position and moves on the horizontal axis.
Cutting Direction:
Vertical Milling Machine: Cutting is done from top to bottom.
Horizontal Milling Machine: Cutting is done horizontally, passing over or under the workpiece.
Areas of Use:
Vertical Milling Machine: It is used for making complex shapes, contours and detailed works. It is especially preferred for drilling, surface treatment and processes requiring fine workmanship.
Horizontal Milling Machine: It is used for processing larger and heavier workpieces. It is especially effective in machining long parts, large surfaces and grooves.
Fixing the Workpiece:
Vertical Milling Machine: The workpiece is usually fixed on the table and the table moves.
Horizontal Milling Machine: The workpiece usually remains stationary and the cutting tool moves along the workpiece.
Cutting Tool Access:
Vertical Milling Machine: Provides better visibility and access, which allows the operator to control the cutting process more easily.
Horizontal Milling Machine: Larger and heavier cutting tools can be used, allowing for heavier cutting operations.
Machine Structure:
Vertical Milling Machine: Generally has a more compact structure and takes up less space.
Horizontal Milling Machine: Generally larger and heavier, which allows for a more robust and stable structure.
Cutting Speed and Power:
Vertical Milling Machine: It can usually cut faster, but is suitable for operations that require less power than horizontal milling machines.
Horizontal Milling Machine: Can perform more powerful and heavy cutting operations, allowing larger materials to be machined.
Application Examples:
Vertical Milling Machine: Mould making, hole making, contour machining, surface treatment.
Horizontal Milling Machine: Machining long parts, grooving, machining large surfaces.
These differences make both machine types more suitable for specific applications and help users choose the right machine for their needs.
The use of a vertical milling machine is as follows.
Preparation:
Fixing the Workpiece: Fix the workpiece in a vice or a suitable clamping device.
Cutting Tool Selection and Assembly: Select the cutting tool suitable for the workpiece and mount it in the tool holder.
Adjusting the Machine:
Cutting Tool Positioning: Adjust the position of the cutting tool relative to the workpiece.
Machining Parameters: Specify and set parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut.
Machining:
Starting the Machine: Start the machine and move the cutting tool towards the workpiece.
Cutting Process: As the cutting tool passes over the workpiece, it removes material to form the desired shape. Check the condition of the cutting tool and workpiece continuously during the process.
Completion:
Finalising the Operation: Stop the machine when the operation is complete.
Removing the Workpiece: Remove the workpiece from the vise and check the operation.
Maintenance of the vertical milling machine is as follows.
Daily Maintenance:
Cleaning: Clean the machine tool and surrounding area after the operation is complete. Use an air gun or brush to remove chips, oil and other debris.
Lubrication: Regular lubrication of moving parts (e.g. slides and screws) is necessary. Do this using lubricants recommended by the manufacturer.
Checks: Check the tightness of cutting tools and tool holders. Tighten any loose parts.
Weekly Maintenance:
Coolant: Check the coolant level and quality. Top up if missing or replace if necessary.
Connections: Inspect the electrical connections and other cables. Check for damage or looseness.
Cleaning: Clean the cutting tool and tool holders.
Monthly Maintenance:
Moving Parts: Make sure all moving parts are in proper working order. Check slides, ball screws and other moving parts for wear and tear.
Hydraulic System: If your machine has a hydraulic system, check the hydraulic oil level and quality. Complete if missing or replace if necessary.
Electric Panel: Open the electrical panel and clean the dust and dirt inside. This will help prevent overheating and malfunctions.
Annual Maintenance:
Calibration: Calibrate or have a professional technician calibrate to maintain machine accuracy.
Part Replacement: Replace worn or frayed parts. This applies to slides, bearings, belts and other important parts.
Detailed Inspection: Make a detailed inspection of the general condition of the machine. If any problems are found, repair or replace as necessary.
Safety Checks:
Emergency Stop: Make sure the emergency stop buttons are working properly.
Protective Covers: Ensure that all protective covers are in place and secure.
Operator Training: Provide regular training for operators to use the machine correctly and safely.
These steps ensure efficient and safe operation of the vertical milling machine and extend the life of the machine.
We provide the fastest service to our customers with our rich spare parts stock and professional service network. Original spare parts are supplied by Foreman instead of third party sellers. You can contact us when you encounter any problems with vertical milling machines.
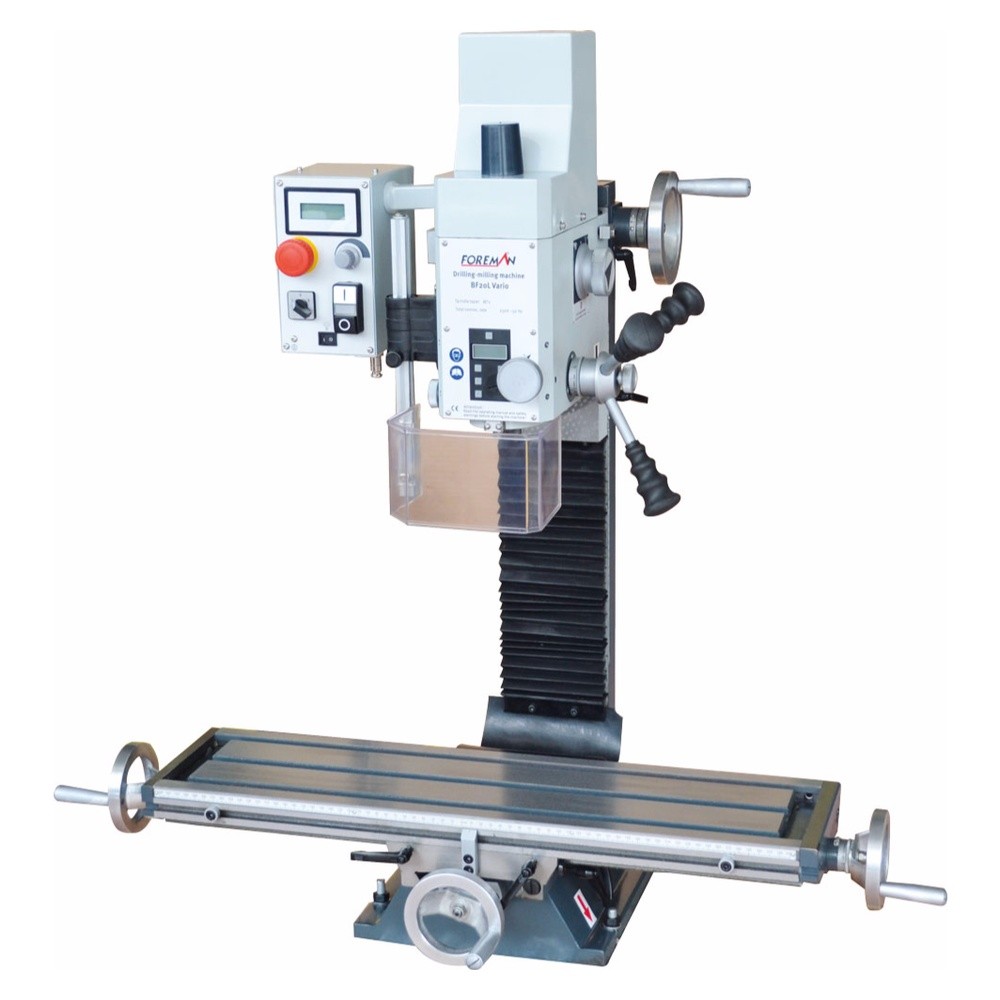
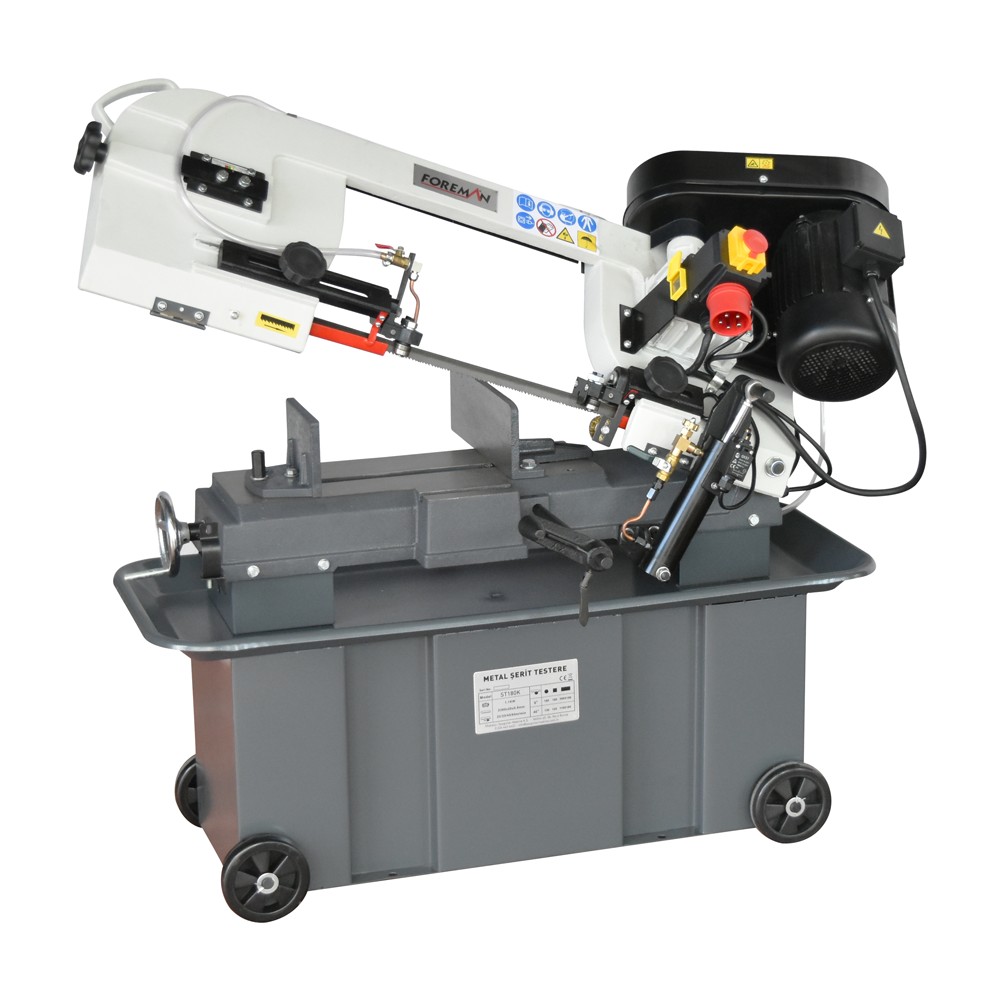














































_zkmmzopp1k.jpg)